골드3 : 그래프 문제이다.
생각
현재 시작 위치에서 다음 쓰레기를 치우고, 그 위치에서 다시 다음 경로를 탐색하는 과정으로 문제를 풀려 했다. 하지만 코드를 짜면서도 탐색과정이 계속하여 중복되서 어떻게 풀어야 할지 고민을 많이했다.
시간 초과 Code
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<list>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<functional>
#define INF 999999999
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PI;
int W, H;
char map[21][21];
int check[21][21];
int dy[4] = {0, -1, 0, 1}, dx[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int ans;
vector<PI> trash;
PI start;
void printMap(){
cout << "Map" << '\n';
for (int i = 0; i < H; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < W; j++) {
cout << map[i][j];
}cout << '\n' << '\n';
}
}
void printCheck(){
cout << "Check" << '\n';
for (int i = 0; i < H; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < W; j++) {
cout << setw(3) <<check[i][j];
}cout << '\n' << '\n';
}
}
void bfs(PI start){
memset(check, -1, sizeof(check));
queue<pair<PI, int>> q;
q.push(make_pair(start, 0));
check[start.first][start.second] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int now_y = q.front().first.first, now_x = q.front().first.second;
int count = q.front().second;
q.pop();
count++;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int next_y = now_y + dy[i], next_x = now_x + dx[i];
if (0 <= next_y && next_y < H && 0 <= next_x && next_x < W && map[next_y][next_x] != 'x') {
if (check[next_y][next_x] == -1) {
q.push(make_pair(make_pair(next_y, next_x), count));
check[next_y][next_x] = count;
}
}
}
}
// printCheck();
}
void go(int depth, PI start, int count){
// printMap();
if (depth == trash.size()) {
ans = min(ans, count);
return;
}
// memset(check, 0, sizeof(check));
for (int i = 0; i < trash.size(); i++) {
int now_y = trash[i].first, now_x = trash[i].second;
if (map[now_y][now_x] == '*'){
bfs(start);
if (check[now_y][now_x] != 0) {
map[start.first][start.second] = '.';
map[now_y][now_x] = 'o';
go(depth+1, trash[i], count+check[now_y][now_x]);
map[now_y][now_x] = '*';
map[start.first][start.second] = 'o';
}
}
}
}
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
while (true) {
cin >> W >> H;
ans = INF;
trash.clear();
if (W == 0 && H == 0) {
return 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < H; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < W; j++) {
cin >> map[i][j];
if (map[i][j] == 'o') {
start = make_pair(i, j);
}
if (map[i][j] == '*') {
trash.push_back(make_pair(i, j));
}
}
}
go(0, start, 0);
if (ans == INF) {
cout << -1 << '\n';
} else {
cout << ans << '\n';
}
}
}그 결과 시간초과가 났다. 그래서 다른 방법을 고민했다.
그래프
o 역시 쓰레기로 본다면 다음과 같은 그림으로 볼 수 있다.
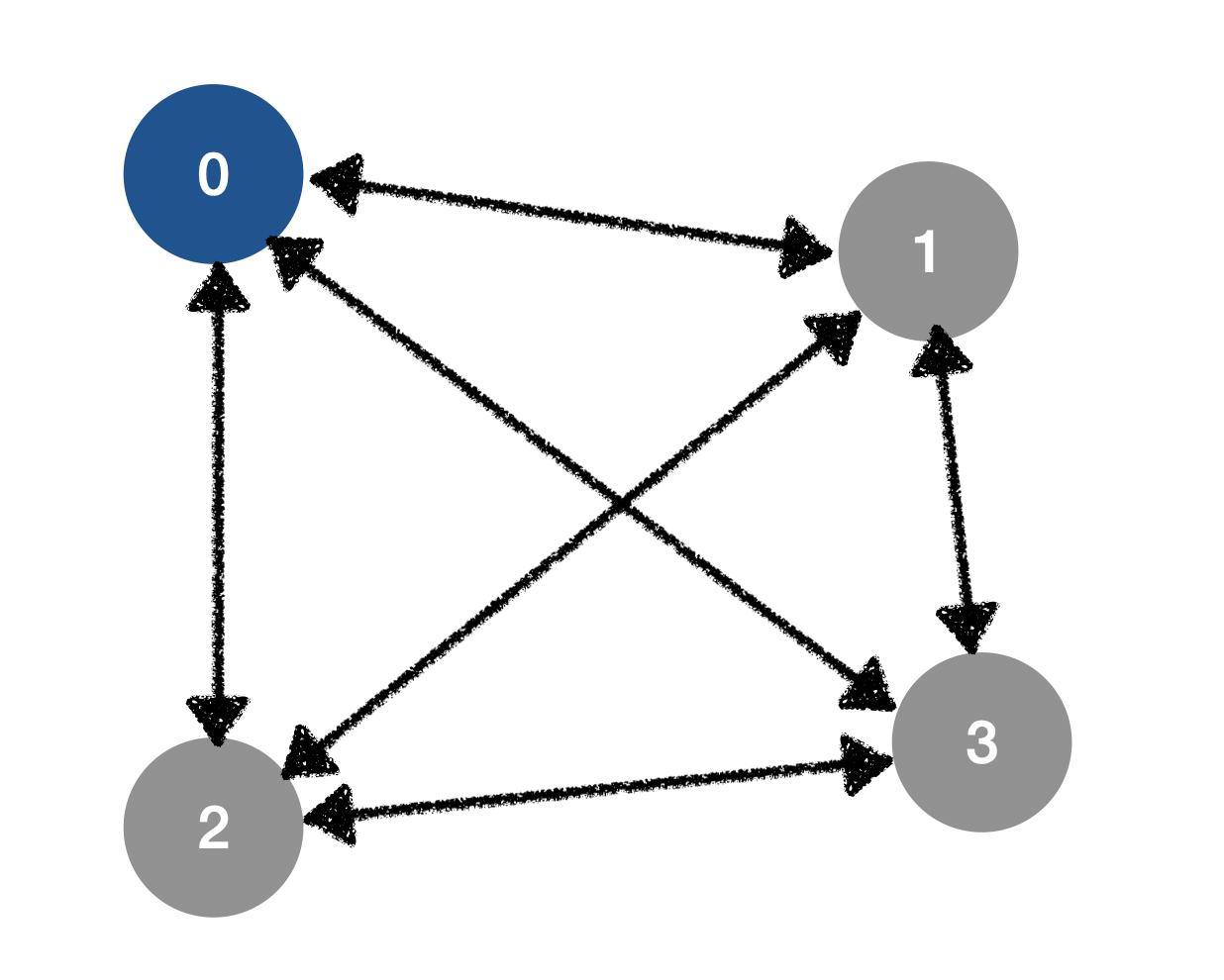
결국, 0번 위치에서 시작하여 나머지 노드들을 전부 순회했을 때, 최소이동 거리를 구하는 문제이다. 이렇게 문제를 모델링할 경우 노드간의 거리를 구하는 과정을 1번만 수행하면 되기 때문에 위에 있는 코드보다 연산이 줄어든다.
7 5
.......
.o...*.
.......
.*...*.
.......
0 4 2 6
4 0 6 2
2 6 0 4
6 2 4 0
해당 입력에 대해 노드와 간선을 구하면 다음과 같이 구해진다. 이제 부터 해야할 일은 0번 부터 출발하여 어떤 순서로 이를 순회할지에 대한 문제이다.
0 1 2 3
0 1 3 2
0 2 1 3
0 2 3 1
0 3 1 2
0 3 2 1
순회하는 방법은 다음과 같이 순열로 구성된다. 0→1→2→3과 같은 방향으로 갔을 때, 이동거리의 최솟값을 구하면 된다.
Code
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<list>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<functional>
#define INF 999999999
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PI;
int N, M;
char map[21][21];
int check[21][21];
int node[11][11];
int dy[4] = {0, -1, 0, 1}, dx[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
vector<PI> trash;
int ans;
void printCheck(){
cout << "Check" << '\n';
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
cout << setw(3) << check[i][j];
}cout << '\n' << '\n';
}
}
void printNode(){
for (int i = 0; i < trash.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < trash.size(); j++) {
cout << setw(3) << node[i][j];
}cout << '\n';
}
}
void bfs(PI start){
queue<PI> q;
q.push(start);
check[q.front().first][q.front().second] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int now_y = q.front().first, now_x = q.front().second;
q.pop();
int count = check[now_y][now_x];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int next_y = now_y + dy[i], next_x = now_x + dx[i];
if (0 <= next_y && next_y < N && 0 <= next_x && next_x < M && map[next_y][next_x] != 'x') {
if (check[next_y][next_x] == -1) {
check[next_y][next_x] = count+1;
q.push(make_pair(next_y, next_x));
// printCheck();
}
}
}
}
}
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
while (true) {
cin >> M >> N;
// 사용하는 배열 초기화
trash.clear();
ans = INF;
memset(node, 0, sizeof(node));
if (M == 0 && N == 0) return 0; // 종료 조건
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
cin >> map[i][j];
if (map[i][j] == 'o') trash.insert(trash.begin(), make_pair(i, j)); // 시작 위치는 0에 고정
if (map[i][j] == '*') trash.push_back(make_pair(i, j));
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < trash.size(); i++) {
memset(check, -1, sizeof(check));
bfs(trash[i]);
for (int j = i; j < trash.size(); j++) {
node[i][j] = check[trash[j].first][trash[j].second];
node[j][i] = check[trash[j].first][trash[j].second];
}
}
// printNode();
vector<int> p; // 순열을 위한 배열 생성
for (int i = 1; i < trash.size(); i++) p.push_back(i);
do{
p.insert(p.begin(), 0); // 시작 위치 추가
int localAns = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < p.size()-1; i++) {
localAns += node[p[i]][p[i+1]];
if (node[p[i]][p[i+1]] == -1) {
ans = -1;
break;
}
}
ans = min(ans, localAns);
p.erase(p.begin()); // 시작 위치 삭제
}while(next_permutation(p.begin(), p.end()));
cout << ans << '\n';
}
return 0;
}Traveling Salesman problem (TSP)
이런 문제는 결국 모든 지점을 지나는데 걸리는 최소 거리를 묻는 문제이다. 이러한 문제는 Traveling Salesman problem (TSP) 라고 불리는 문제로 computer science 분야에서 가장 중요하게 취급되는 문제 중 하나이다. 비슷한 문제로는 백준(2098번) - 외판원 순회가 있다.