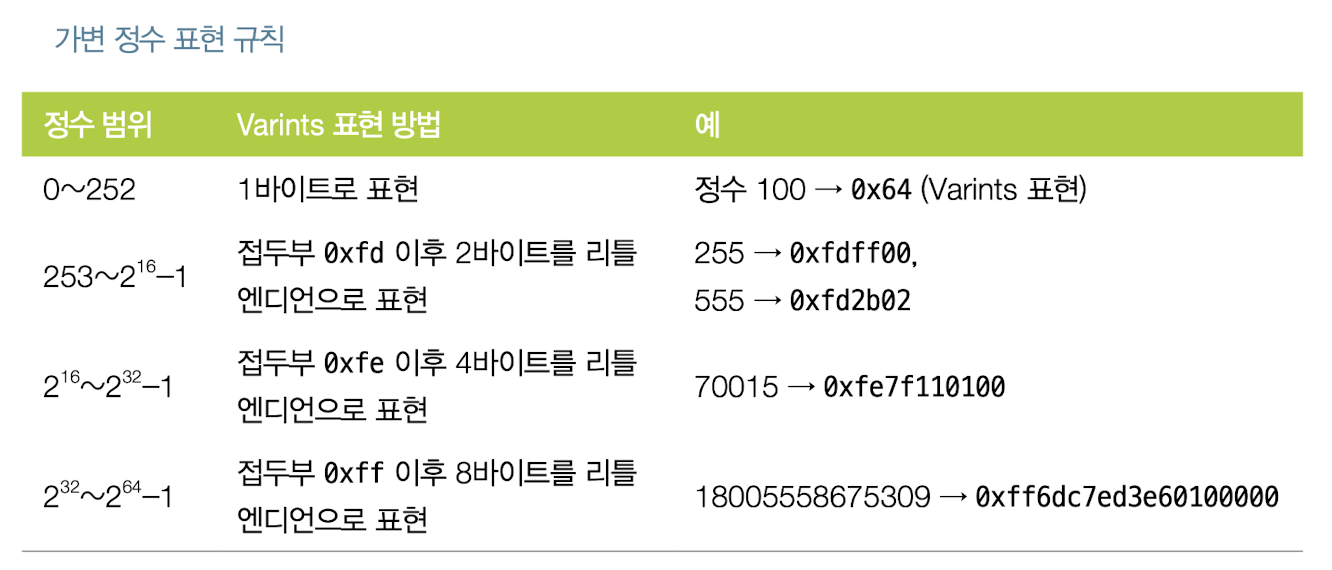
가변적인 수를 Encoding하는 방법 중 하나인 Varints 형식을 알아보자.
Varint
- 이전에 Input, output등의 개수를 나타낼 때 있어 varint 형식을 사용한다고 했었다.
- 여기서 간단하게 알아보자.
def read_varint(s):
'''read_varint reads a variable integer from a stream'''
i = s.read(1)[0]
if i == 0xfd:
# 0xfd means the next two bytes are the number
return little_endian_to_int(s.read(2))
elif i == 0xfe:
# 0xfe means the next four bytes are the number
return little_endian_to_int(s.read(4))
elif i == 0xff:
# 0xff means the next eight bytes are the number
return little_endian_to_int(s.read(8))
else:
# anything else is just the integer
return i
def encode_varint(i):
'''encodes an integer as a varint'''
if i < 0xfd:
return bytes([i])
elif i < 0x10000:
return b'\xfd' + int_to_little_endian(i, 2)
elif i < 0x100000000:
return b'\xfe' + int_to_little_endian(i, 4)
elif i < 0x10000000000000000:
return b'\xff' + int_to_little_endian(i, 8)
else:
raise ValueError('integer too large: {}'.format(i))